DC Motor Yibin Tianruida Auto Parts Co.,Ltd , https://www.trdautoparts.com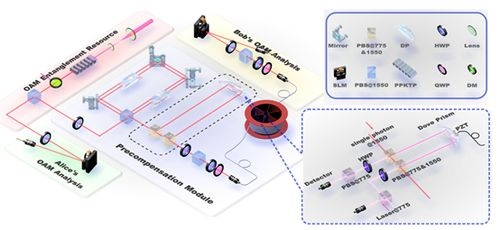
China University of Science and Technology Achieves High-Dimensional Quantum Entanglement Distribution with a Distance of One Kilometer
[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] Guo Guangcan, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and a professor at the University of Science and Technology of China, has made new progress in quantum communication experiments. The team's Li Chuanfeng and Huang Yunfeng's research team collaborated with Jinan University professor Li Zhaohui and Sun Yat-sen University professor Yu Siyuan to realize the entanglement distribution of angular momentum in 3D orbits. The research results were published in the international optical journal Optica on March 12.
Quantum entanglement is an important resource for quantum information processes such as quantum communication, quantum precision measurement, and quantum computing. Its long-distance distribution is essential for the practicality of quantum technology and the inspection of basic problems in quantum physics. In quantum mechanics, when several particles interact with each other, because the characteristics possessed by each particle have been integrated into the overall nature, it is not possible to describe the properties of each particle alone, but only the properties of the overall system, this phenomenon is called quantum Entanglement or quantum entanglement. Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon that occurs purely in quantum systems; no similar phenomenon can be found in classical mechanics.
High-dimensional systems have higher channel capacity, stronger anti-eavesdropping capabilities, and more efficient quantum computing capabilities. The orbital angular momentum of photons is a high-dimensional system that has been widely concerned in recent years, and has advantages in dimensional scalability. However, the orbital angular momentum entanglement is easily affected by atmospheric turbulence or mode crosstalk and mode dispersion in the optical fiber. Before that, it could only transmit a few meters distance, and was limited to the distribution of two-dimensional entanglement.
Aiming at the problems faced in the entanglement distribution of high-dimensional orbital angular momentum, the research group of Li Chuanfeng and Huang Yunfeng cooperated with the research group of Jinan University and Sun Yat-sen University to independently develop a few-mode fiber suitable for photon space division multiplexing, and designed orbital angular momentum mode dispersion The pre-compensation device realizes the distribution of three-dimensional orbital angular momentum entangled photon pairs in a 1 km fiber for the first time. The distributed quantum states were verified by the generalized Bell's inequality (CGLMP inequality), and three standard deviation inequality violations were obtained, which verified the high-dimensional nonlocality of the quantum states. In theoretical physics, Bell's inequality is an inequality about the existence of a complete local hidden variable theory. Experiments show that Bell's inequality is not valid, indicating that there is no physical theory about local hidden variables that can replicate every prediction of quantum mechanics (ie Bell's theorem).
Aiming at the mode dispersion and decoherence characteristics of optical fibers, the research group also proposed an implementation scheme to further expand its dimensions and transmission distance. This work provides the possibility for the realization of long-range high-dimensional quantum information tasks using spatial pattern reuse technology.
Source: University of Science and Technology of China, Encyclopedia