Deep Groove Ball Bearing Inch R Series is the most common type of rolling bearings, a wide range of uses. The basic type of Deep Groove Ball Bearing consists of an outer ring, an inner ring, a Steel Ball and a group of cage. Deep Groove Ball Bearing Inch R Series Deep Groove Ball Bearing Inch R,Non-Standard Ball Bearing,Stainless Steel Ball Bearing,Inch Size Ball Bearing NINGBO FANGXING IMPORT& EXPORT CO.,LTD. , https://www.fxbearings.com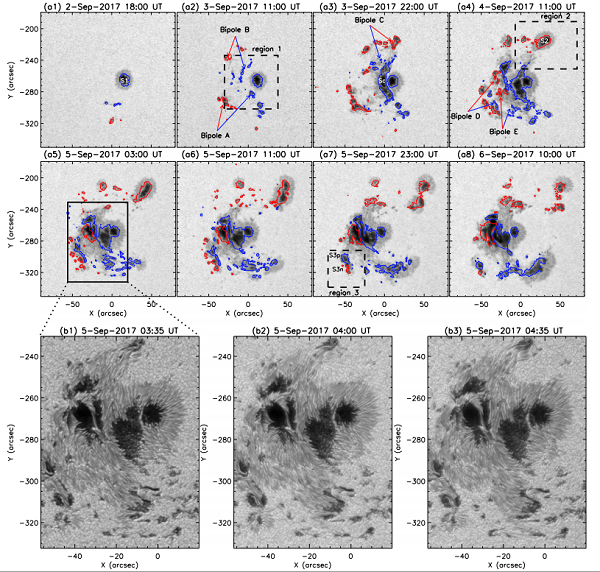
According to the size of deep groove ball bearings can be divided into:
(1) miniature bearings - nominal diameter size range of 26 mm below the bearing;
(2) small bearings - nominal diameter size range of 28-55 mm bearing;
(3) small and medium sized bearings - nominal diameter size range of 60-115 mm bearing;
(4) in the large bearing - nominal diameter size range of 120-190 mm bearing
(5) large bearings - nominal diameter size range of 200-430 mm bearing;
(6) extra large size bearing, nominal diameter range of 440 mm or more.
Yunnan Observatory Makes Progress in Studying Sunspot Penumbra Formation and Decline
[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] Dr. Li Qiaoling, Ph.D. of Sun Observation and Research Base of Fuxian Lake, Yunnan Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Researcher Yan Xiaoli, etc., made new progress in the research of the formation and disappearance process of the 12673 sunspot penumbra in the solar active area. Published on the 3rd in The Astrophysical Journal.
Mature sunspots generally consist of a dark nucleus in the center (umbra) and a slightly brighter halo (penumbra) in the periphery. The appearance of sunspot penumbra is the standard to distinguish ordinary sunspots from small pores. The sunspot is a strong magnetic field on the surface of the sun. When there are many sunspots on the surface of the sun, other solar activities are also frequent. Sunspots are the object of studying the hydrostatic equilibrium, and by studying the evolution of sunspots, we can understand the relationship between sunspots and other solar activity phenomena, which is of great significance for exploring and predicting solar burst activity.
Using the observation data from the Chengjiang Fuxian Lake One-meter New Vacuum Telescope (NVST) and the American Solar Dynamics Satellite (SDO), they conducted a detailed study of the evolution of sunspots in active zone 12673. Through the analysis of sunspot penumbra evolution during sunspot penumbra evolution, it is found that as the sunspot penumbra area increases, the transverse field intensity of the sunspot penumbra field increases and the longitudinal field intensity decreases. In the process of the penumbra disappearing, the transverse field intensity of the sunspot penumbra magnetic field decreases and the longitudinal field intensity increases. The newly emerged magnetic current tube is suppressed and converged by the existing magnetic field to form the sunspot penumbra. The sunspot pendant magnetic field changes from horizontal to vertical under the action of the new floating magnetic current, which will cause the sunspot penumbra to disappear, as shown in the figure. .
Through the evolution analysis of the sunspot velocity field during the sunspot evolution, it is found that with the formation of the sunspot penumbra, the moat flow around the sunspot periphery gradually appears. During the black penumbra decay, the velocity of the material flow near the side of the new floating magnetic current zone gradually decreases and disappears. At the same time, it was also found that the magnetic field environment around sunspots has an impact on the lifespan of sunspots, and the sunspots near the flare burst have a shorter lifespan.
The research results were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, key projects, and key projects in Yunnan Province.