95% of China's energy and 85% of raw materials come from mineral resources. With rapid population expansion and economic development, the demand for mineral resources is growing. At the same time, along with the exploitation and development of the mine, a large amount of tailing water will be produced. Tailings water is the main component in the tailings slurry after solid ore dressing . When the tailings slurry is transported to the tailings pond, it is self-gravity sorted and precipitates the tailings water. The annual discharge of tailings water in China is about 3.6 billion, and most of them are not directly processed and stored directly in the tailings dam. A copper- molybdenum plant adopts a grinding-mixing flotation-separation separation process. After one rough selection, one sweep and three times, a copper-molybdenum mixed concentrate is obtained, and finally copper-molybdenum separation is performed. The mine is located in arid and rain-free areas, and water resources have always been a bottleneck restricting the development of enterprises. A large amount of tailings water is accumulated in the tailings dam, which makes the water resources more difficult. At the same time, it also occupies a large amount of land, causing serious pollution to the surrounding environment and posing a major threat to people's life and health. Therefore, the study of tailings water treatment and the use of tailings backwater has become a major problem that the concentrator needs to solve urgently. Tailings water purification refers to the physical and chemical treatment of harmful substances in the ore water, so that the content is reduced to meet the requirements for reuse or discharge. The purification method of tailings water depends on the composition and quantity of harmful substances, the type of water discharged into the water system, and the requirements for the quality of the return water. The common methods are: 1 natural precipitation. The tailings granules in the tailings slurry are removed using a tailings pond or other sedimentation tank. 2 physical chemical purification. Some harmful substances are removed by using an adsorbent material. 3 chemical purification. Add appropriate amounts of chemicals to promote the conversion of harmful substances into harmless substances. After the tailings water is purified and returned to the water, it can not only alleviate the contradiction of water shortage in the plant, but also solve the problems of environmental protection and safety. The recycling of tailings water is the focus of wastewater treatment technology at home and abroad. Common methods are: 1 returning water from the concentration pool. In order to save new water consumption, tailwater dewatering facilities such as tailings concentration tanks or inclined plate concentration tanks are often built in or near the plant for tailings dewatering. The tailings sand sinks to the bottom of the concentration tank, and the clarified water overflows from the pool. Return to the factory for reuse. The return water of the concentration tank can generally reach 40% ~ 70%. 2 tail mines back to the water. After the tailings are discharged into the tailings pond, part of the water content in the tailings slurry remains in the voids of the sedimentary tailings. Some of them are naturally clarified in the tailings pond, degrading toxic and harmful substances, and the other part is evaporated in the reservoir. The backwater from the tailings pond is to recover the remaining part of the clarified water for use in the selection plant. First, the experimental method The final tailings water quality test result of the copper-molybdenum concentrator was dark gray with a turbidity of 49.4 and a pH of 13. The paper uses new water, untreated tailings backwater, treated tailings backwater for ore dressing test, and compares the ore dressing effect. Second, the test results (1) The new water test uses fresh water for flotation tests. (2) Untreated tailings backwater test, using untreated tailings backwater for flotation test, untreated tailings backwater makes the grade and recovery rate of molybdenum concentrate slightly lower, and because The untreated tailings backwater contains a large amount of Na2S. When the tailings water is returned to the process, it inhibits the copper minerals, so the qualified copper concentrate cannot be obtained, and the copper concentrate recovery rate is low. This is why the tailings water cannot be returned directly to the process. (C) tailings backwater test after anionic flocculant treatment The main body of the anionic flocculant is based on polyacrylamide, and the bridging group is an anion. The anionic flocculant is directly added to the tailings water for treatment, and then the treated tailings water is used for the test. After the tailings water treated by the anionic flocculant is tested, the grade of the molybdenum concentrate is decreased, and the grade of the copper concentrate is The recovery rate is slightly improved, and the sorting effect is close to that of untreated tailings. (IV) Tailings backwater test after cationic flocculant treatment The main body of the cationic flocculant is based on polyacrylamide, and the bridging group is a cation. The cationic flocculant is directly added to the tailings water for treatment, and then the treated tailings water is used for the test. The tailings backwater after the treatment with the cationic flocculant is tested to obtain the grade and recovery of the molybdenum concentrate and after the anion treatment. The data obtained from the tailings backwater test did not differ much. The recovery rate and grade of copper and molybdenum fluctuated within a small range, and the test results were still not satisfactory. (E) by KMG test tailings return after treatment KMG Kunming Research Institute of Metallurgy of an organic agent, the agent into a polymer main component polysaccharide, non-toxic source of extensive, inexpensive, and apparently The polymer flocculant is similar and has a bridging action to flocculate the suspended matter in the liquid. Another important feature of the agent is its ability to adsorb certain substances in the slurry. The direct addition of KMG to the tailings water reduces the pH of the tailings water and eliminates residual sodium sulfide and suspended solids in the liquid. Using the tailings backwater treated with water treatment agent KMG, the obtained molybdenum concentrate and copper concentrate index are better than the tailings backwater index treated with anionic or cationic flocculant, and the index of using new water beneficiation. similar. Therefore, KMG can be used to treat tailings water and return to the process. (6) Closed-circuit test using tailings backwater after treatment with KMG, closed-circuit experiments on the basis of open-circuit closed-circuit experiments using KMG-treated tailings water back for closed-circuit test, obtaining a molybdenum concentrate grade of 48.53%, The recovery rate is 90. 96%, copper content is 0.50%, copper concentrate grade is 19.23%, recovery rate is 88. 50%, copper concentrate contains molybdenum 0. 19% satisfactory index, further proves KMG treated tailings The water is suitable for returning to the plant for research purposes. III. Conclusion 1. A copper-molybdenum plant adopts a grinding-mixing flotation-separation process to obtain a copper-molybdenum mixed concentrate through a coarse-sweeping three-preparation, and finally a copper-molybdenum separation. The tailings of the plant have high alkalinity and high content of sodium sulfide. If directly returned to use, it will have a certain inhibitory effect on copper minerals. The tailings backwater test showed that the untreated tailings backwater and the tailings backwater test treated with anionic flocculant or cationic flocculant failed to obtain the ideal test results. The tailings backwater test using KMG can obtain 45.36% of molybdenum concentrate grade, recovery rate of 80.23%, copper content of 0.69%, copper concentrate grade of 22.24%, recovery rate of 74.08%, and molybdenum content of 0.19%. Better indicator. 2. The treatment and reuse of tailings wastewater can achieve comprehensive utilization of backwater under lower cost conditions, with high economic and social benefits.
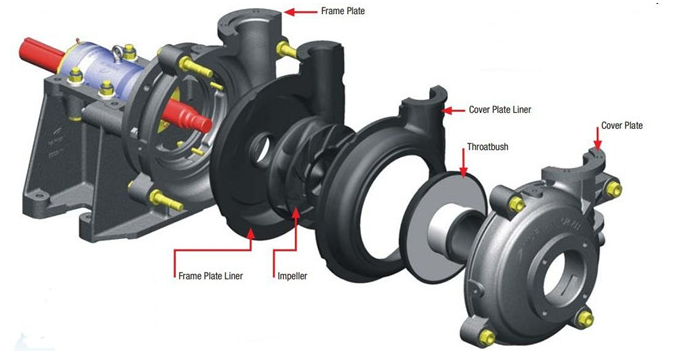
1. Naipu Pump offers all elastomer rubbe wet parts.The
high chrome white iron is a very good wear-resistant material and nice
wear-resistant is our slurry pumps important character.For the corrosive
slurries with blunt particles, we recommend the natural rubber.
2. Material of Slurry Pump Wet End Parts:
Natural rubber,butyl,neoprene,hypalon,etc.
Slurry Pump Parts, Rubber Slurry Pump Parts, Slurry Pump Rubber Parts, Slurry Pump Impeller Shijiazhuang Naipu Pump Co., Ltd. , https://www.naipu-pump.com